Other informations
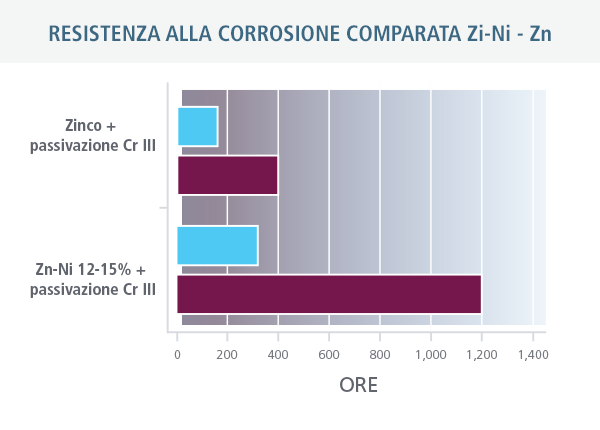
Hours spent before white and red corrosion compared between the twoncoatings Increased wear resistance: a hard and thin Zn-Ni coating has a uniform and smooth finish that increases wear resistance,reducing both friction and the possibility of abrasion.
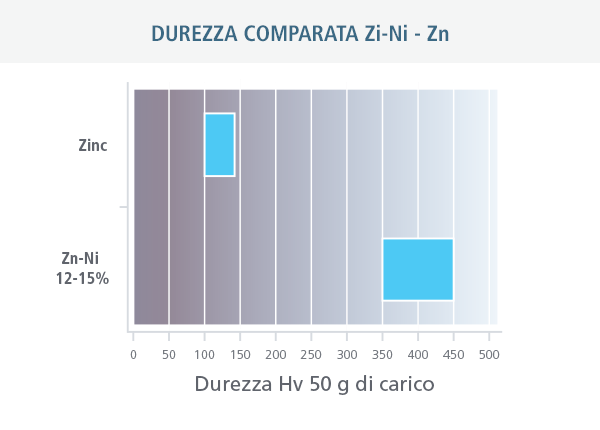
On the Vickers hardness scale, the parts coated with Zn-Ni also reach 450 Hv, compared to less than 150 for parts coated with zinc.
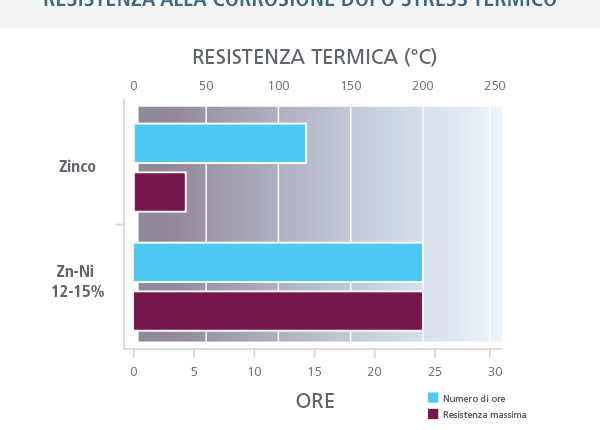
Resistance to thermal stress: zinc nickel coatings provide greater protection against thermal stresses. The tests show that the components coated with Zn-Ni maintain their resistance to corrosion, despite exposure to thermal stresses up to 300 ° C. The parts coated with zinc instead resist thermal stresses up to only 120 ° C and then lose corrosion resistance.
Successful cases
Zn-NiI zinc nickel coatings can provide a much higher degree of substrate protection, which means that they can withstand the stresses that inevitably shorten the life of the components, from equipment with moving parts to buildings and infrastructure .
There are some industries, including the automotive and aerospace industries, have already widely adopted these coatings. Others, such as constructors of construction, agriculture and power transmission equipment, are beginning to exploit them to protect the value of their products. Agricultural and construction equipment is continuously exposed to time and often to corrosive fertilizers, herbicides and road chemicals.
Zn-Ni-treated carbon steel can also be used to replace more expensive materials used to resist corrosion. In many industries, machine builders have replaced it with stainless steel to increase corrosion resistance. Carbon steel with Zn-Ni coating can reduce component weight as well as control costs.